In the DRUG SAFETY/PATIENT SAFETY [07] dashboard you see in the left window an overview of the Adverse Events for each of your drugs or products in a clinical trial or on the market.
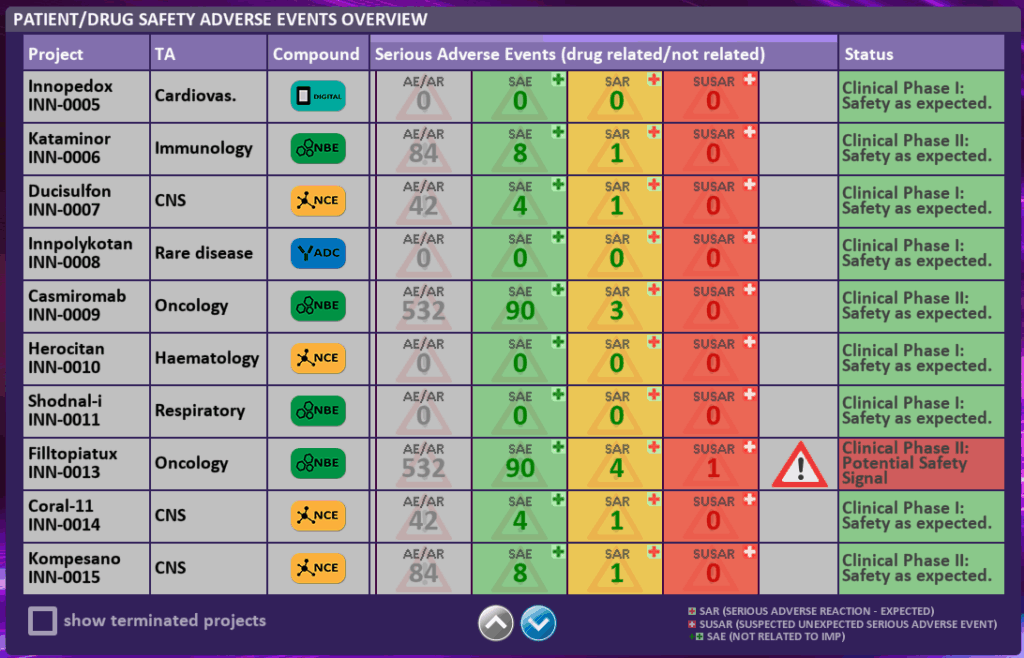
This includes Adverse Events, Serious Adverse Events, Serious Adverse Reactions and SUSARs.
A caution sign  will appear if a potential safety signal is detected. Safety signals may indicate a risk to patients or trial success. By clicking on a specific project, you get additional detailed project information, and you also will have the option to put a project on “hold” or “terminate” a project. (see project dashboard in FUNCTIONAL DASHBOARDS [03]).
will appear if a potential safety signal is detected. Safety signals may indicate a risk to patients or trial success. By clicking on a specific project, you get additional detailed project information, and you also will have the option to put a project on “hold” or “terminate” a project. (see project dashboard in FUNCTIONAL DASHBOARDS [03]).
How are Adverse Events classified?
You see an explanation in the window on the right.
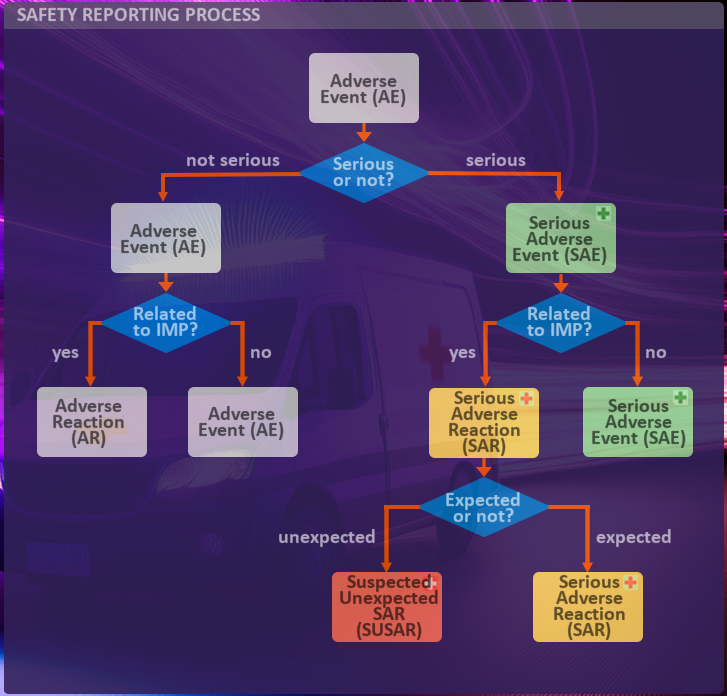
| Adverse Event (AE) | An Adverse Event is an untoward medical occurrence after exposure to a medicine, which is not necessarily caused by that medicine. An adverse event can therefore be any unfavorable and unintended symptom or sign (including e.g. an abnormal laboratory finding) or disease temporally associated with the use of a medicinal (investigational) product, whether or not related to the medicinal (investigational) product. |
| Adverse Reaction (AR) | Adverse Reactions are Adverse Events judged to be related to the investigational medicinal product. |
| Serious Adverse Event (SAE) | Serious Adverse Event (SAE) is identified as any untoward medical occurrence during a human drug trial at any dose that results in death, is life-threatening, requires inpatient hospitalization or causes prolongation pf existing hospitalization, results in persistent or significant disability/incapacity, may have cause a congenital anomaly/birth defect or requires intervention to prevent permanent impairment or damage. |
| Serious Adverse Reaction (SAR) | Serious Adverse Reactions are Serious Adverse Events judged to be related to the investigational medicinal product. |
| Suspected Unexpected SAR (SUSAR) | If a SAR is unexpected, it’s called a Suspected Unexpected Serious Adverse Reaction (SUSAR). This means the reaction’s nature or severity doesn’t align with the drug’s known safety profile (including labeling and the investigator’s brochure). SUSARS must be reported to the relevant drug regulation authority. |
| The Drug Safety/Patient Safety function plays a crucial role in drug development, ensuring the safety of both the investigational drug and the patients participating in clinical trials. Responsibilities are collecting and analyzing safety data, identifying signals, assessing risk-benefit profile and communicating safety information to relevant stakeholders (e.g. regulatory authorities). |